What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) stands as a critical component to drive organic traffic to your website. While content and backlinks play significant roles, Technical SEO lays the foundation for a well-optimized site. This guide will cover the essential aspects of Technical SEO, from basic concepts to advanced strategies.
What is Technical SEO?

Technical SEO refers to optimizing your website’s infrastructure to enhance its visibility in search engine results. Unlike on-page SEO, which focuses on content, and off-page SEO, which revolves around backlinks, Technical SEO ensures that search engines can crawl and index your site effectively.
Benefits Why is Technical SEO Important?

Technical SEO is a crucial aspect of digital marketing that significantly impacts a website’s visibility, user experience, and ultimately, its ability to generate revenue through platforms like Google AdSense. At its core, technical SEO involves optimizing the backend structure and technical elements of a website to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank the content. This foundation is essential because no matter how high-quality the content is, if search engines cannot properly access or understand it, the site will struggle to appear prominently in search results, limiting organic traffic and potential ad impressions. One of the primary benefits of technical SEO is improved site performance and speed. Fast-loading pages provide a better user experience, reduce bounce rates, and are favored by Google’s ranking algorithms. Since AdSense revenue depends heavily on site traffic and user engagement, faster sites tend to generate higher ad impressions and clicks, resulting in greater earnings. Additionally, technical SEO ensures that websites are mobile-friendly, which is essential given the increasing dominance of mobile browsing. Responsive designs and mobile optimization help retain visitors and support seamless ad delivery on all device types, enhancing AdSense monetization opportunities.
Key Components of Technical SEO

- Key components of technical SEO form the backbone that ensures a website’s content is discoverable, indexable, and ranks well on search engines, which is critical for maximizing traffic and Google AdSense revenue. One fundamental element is site crawlability, which allows search engine bots to navigate and understand the structure of a website. Using well-configured robots.txt files and XML sitemaps, publishers guide crawlers to essential pages while preventing access to duplicate or irrelevant content, streamlining indexing for improved search rankings. Crawl errors, such as broken links or dead ends, must be regularly identified and fixed to maintain smooth bot access and user experience, which directly impacts organic traffic volume.
- Another key component is website speed optimization. Page loading times are a significant ranking factor in Google’s algorithm and heavily influence visitor engagement. Enhanced speeds reduce bounce rates and encourage longer sessions, increasing the number of AdSense ad impressions and click opportunities. Techniques to improve speed include compressing images, minimizing code (CSS, JavaScript, HTML), leveraging browser caching, and using content delivery networks (CDNs) that distribute content globally to reduce latency. A mobile-friendly responsive design is also essential as mobile traffic dominates web usage. Mobile optimization ensures ads display correctly and load quickly on smartphones and tablets, which supports AdSense monetization effectiveness.
2. Mobile Optimization

Mobile optimization is a crucial aspect of maximizing Google AdSense revenue, as mobile devices now account for the majority of internet traffic and ad interactions. A mobile-optimized site ensures that content and ads display correctly and load quickly on smartphones and tablets, creating a seamless user experience that encourages longer visits and more ad impressions. Responsive design is the foundation of mobile optimization, allowing websites to automatically adjust their layout to fit varying screen sizes without sacrificing functionality or aesthetics. This includes adapting ad units to be responsive so they fit into mobile layouts without causing disruption or requiring excessive scrolling. Fast page loading is equally essential because mobile users often browse on the go, with expectations for pages to load within seconds; slow load times increase bounce rates and reduce ad engagement, directly impacting AdSense earnings. Clear and easily tappable call-to-action (CTA) buttons and menus enhance navigation on smaller screens, helping users reach desired content swiftly and interact with ads naturally. Google recommends testing ad placements on mobile regularly, avoiding large leaderboard ads that may not render well, and hiding sidebar ads on mobile as they tend to be pushed down and ignored. Instead, placing ads within content areas—such as above the first paragraph or between content sections—can maximize visibility and click-through rates for mobile users.
3. Page Speed
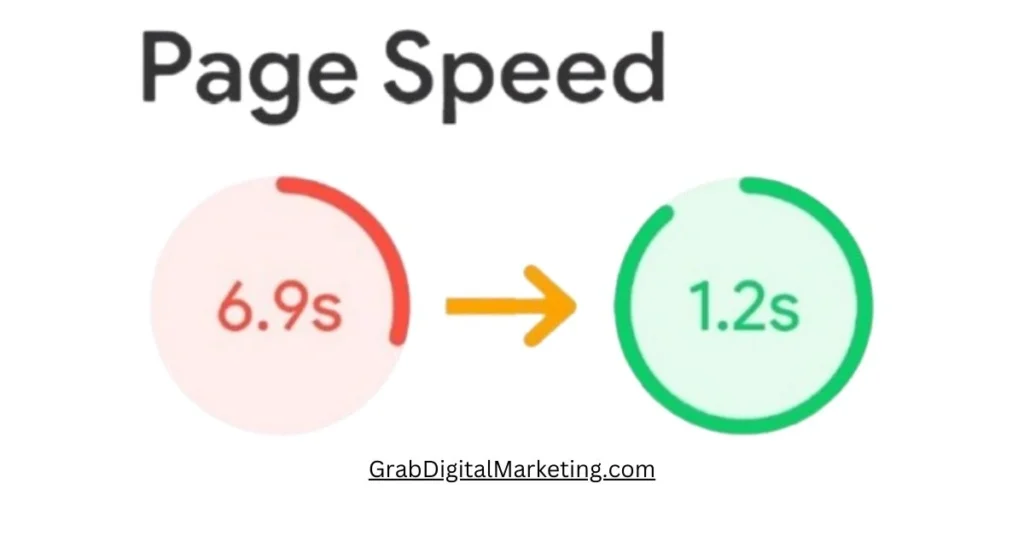
- Page speed is a critical factor in optimizing a website’s performance and maximizing Google AdSense revenue. A faster-loading website provides a better user experience, reducing bounce rates and encouraging visitors to stay longer, which increases the number of ad impressions and potential clicks—both essential to boosting AdSense earnings. Slow page speeds can frustrate users and cause premature site exits before ads have even loaded, diminishing engagement and revenue opportunities. Google actively considers page speed as a ranking signal for search results, meaning faster sites are more likely to appear higher in search rankings, attracting more organic traffic that can positively impact AdSense revenue.
- Page speed optimization involves multiple technical strategies such as compressing images, minimizing JavaScript and CSS files, and leveraging browser caching to reduce load times. It’s also important to optimize the order in which page elements load, prioritizing visible content above the fold while deferring secondary content and ads. Employing asynchronous loading of AdSense scripts ensures that ads do not block the primary content rendering, allowing the page to become interactive more quickly without sacrificing ad visibility. Using content delivery networks (CDNs) stores website data across multiple global servers, reducing latency and speeding up load times for users regardless of their location.
4. HTTPS and Security

- HTTPS and security are fundamental components for any website monetizing with Google AdSense, as they directly influence user trust, search engine rankings, and overall ad performance. HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, encrypts data exchanged between the user’s browser and the website, protecting sensitive information from being intercepted or tampered with by malicious actors. Google prioritizes HTTPS-enabled sites in its search ranking algorithm, considering site security as a positive ranking factor. This means websites using HTTPS generally achieve better visibility in search results, attracting more organic traffic—a critical driver for increasing AdSense impressions and earnings.
- Beyond search rankings, HTTPS instills confidence in visitors, signaling that the site is trustworthy and safe to browse. This trust encourages longer visits and higher user engagement, which increases the likelihood of users interacting with ads. Visitors are also more likely to return to and recommend secure websites, contributing to sustained traffic growth and enhanced monetization opportunities. Moreover, secure sites reduce the risk of malicious code or ad fraud that could damage a publisher’s reputation or violate AdSense policies, which can lead to account suspensions or revenue loss. Implementing HTTPS thus protects not only users but also the publisher’s relationship with Google’s advertising program.
5. Structured Data
Structured data is a powerful SEO tool that enhances how search engines like Google understand, categorize, and display the content of a website, significantly benefiting Google AdSense publishers. By adding structured data markup—commonly using schema.org vocabulary—to the HTML of web pages, publishers provide explicit information about the nature and meaning of their content, such as products, events, reviews, recipes, or articles. This semantic clarity helps search engines interpret the content more accurately, allowing for improved indexing, better search visibility, and the potential to appear in rich search results or rich snippets. These enhanced listings often include additional elements like star ratings, images, pricing, and other relevant details that make search results more attractive and engaging to users. For AdSense publishers, structured data contributes indirectly to revenue growth by boosting click-through rates (CTR) on their organic search traffic, which increases the number of visitors who view ads. Rich results stand out visually on search engine results pages (SERPs), attracting more clicks than standard blue links. Increased user engagement and longer site visits foster better monetization opportunities through Google AdSense ads placed on highly trafficked, authoritative pages.
6. Canonicalization

- Canonicalization is a fundamental concept in SEO that helps website owners manage duplicate or similar content by specifying the preferred or “canonical” version of a webpage to search engines. When multiple URLs contain nearly identical or redundant content, search engines can become confused about which version to index and rank. This can dilute the SEO value of the content and negatively impact its visibility in search results. Implementing canonical tags allows publishers to direct search engines to treat one URL as the authoritative source, consolidating ranking signals such as backlinks and user engagement to that preferred version.
- The canonical tag, placed within the HTML head of a page, looks like this: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/preferred-page/” />. This tag informs search engines that all duplicate or similar pages should be considered variations of the indicated canonical URL, which helps focus SEO power and ensures the right version appears in search results. This is especially critical for websites with complex structures or product pages featuring filters, variations, or tracking parameters that can generate multiple URLs for identical content.
7. 404 Errors and Redirects

- 404 errors and redirects play a crucial role in maintaining a website’s health, user experience, and Google AdSense performance. A 404 error occurs when a visitor or search engine bot tries to access a page that no longer exists or has been moved without proper redirection. These errors can frustrate users, lead to lost traffic, and negatively impact SEO rankings, all of which reduce the potential for ad impressions and clicks essential for AdSense revenue. If Google’s AdSense crawler frequently encounters 404 errors on your site, it may have difficulty indexing your content properly, resulting in less relevant ads being served or even a drop in ad delivery, directly affecting earnings.
- To mitigate these issues, effective use of redirects—particularly 301 redirects—is essential. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from an old URL to a new one, ensuring that both users and search engines are automatically sent to the correct page. This preserves SEO value, consolidates link equity, and maintains a seamless user experience across site updates or content reorganization. Proper redirects ensure that visitors don’t encounter dead ends, which keeps engagement high, encourages more interaction with ads, and reduces bounce rates that Google factors into ranking and ad serving decisions.
8. Log File Analysis

- Log file analysis is an essential practice for website owners, especially those using Google AdSense, to gain detailed insights into how search engine bots and users interact with their site. A log file records every visitor’s request to the server, including details about the URL requested, the time of access, HTTP status codes, user agents (such as Googlebot), and response times. Analyzing these logs helps publishers understand which pages are being crawled by search engines like Google, how often they are visited, and whether there are any crawling issues or server errors preventing content from being properly indexed.
- For AdSense publishers, log file analysis reveals critical data that can optimize both SEO and ad monetization. By identifying frequently crawled pages, publishers can ensure their most valuable content and highest-performing AdSense-enabled pages are receiving appropriate attention from Googlebot, which improves search visibility and ad impressions. Conversely, it helps detect crawls wasted on low-value or duplicate pages, allowing publishers to refine site structure or implement canonicalization and noindex tags to focus crawl budgets more effectively.
9. International SEO

- International SEO is vital for publishers using Google AdSense who want to expand their reach to global audiences and maximize revenue across different countries and languages. It involves optimizing the website so that search engines understand which audience to serve based on factors like language and geographic location, thereby improving visibility in regional search results. A key practice in international SEO is the implementation of region-specific URLs using country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs), subdomains, or subdirectories. These structures signal search engines about the target market for each version of the site, aiding in relevance and preventing duplicate content issues. Additionally, hreflang tags play a crucial role in letting search engines know what language and regional version to display to different users, ensuring the right audience receives the correct localized content and avoiding penalties for duplicate or conflicting content.
- Localizing content is another cornerstone of international SEO, going beyond language translation to include cultural adaptations that reflect local preferences, buying habits, and norms. This level of tailoring builds trust with the audience, reduces bounce rates, and enhances user engagement metrics—important factors that influence organic rankings and AdSense monetization potential. Market research to understand user behavior, search patterns, and competitive landscape in each region is critical for developing effective keyword strategies and content plans tailored to local audiences.
Tools for Technical SEO

- Technical SEO tools are invaluable assets for Google AdSense publishers aiming to optimize their websites for better search engine visibility, user experience, and ad revenue. Among the most essential tools are Google’s own offerings like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, PageSpeed Insights, and Mobile-Friendly Test. Google Search Console helps publishers monitor site performance, identify indexing issues, and track keyword rankings, enabling them to address crawl errors and optimize content for higher organic traffic, which can significantly boost AdSense impressions and earnings. Google Analytics provides deep insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion paths, allowing publishers to tailor content and ad placements to maximize user engagement and click-through rates.
- PageSpeed Insights evaluates website speed and offers actionable recommendations to enhance page load times—a crucial factor that affects bounce rates and overall AdSense performance. Mobile-Friendly Test ensures that sites provide an optimal user experience on mobile devices, an audience segment critical for AdSense monetization due to the growing dominance of mobile traffic. Other useful third-party tools include SEMrush and Ahrefs, which offer comprehensive SEO audits, keyword research, competitive analysis, and backlink tracking to help publishers improve site authority and content relevance, driving more qualified traffic to AdSense-enabled pages.
Conclusion
Technical SEO is the backbone of a well-optimized website. By paying attention to the elements discussed in this guide, you can improve your site’s visibility, user experience, and sometimes, your search engine rankings. Remember, SEO is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and updates. Stay ahead of the curve by keeping up with the latest trends and best practices in Technical SEO.

