What is On Page SEO?
On-page SEO, or on-site SEO, refers to optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of a page, unlike off-page SEO, which affects external signals such as backlinks.
Table of Contents
1. Content Quality

content quality is a cornerstone of success for any website, especially for those monetizing through Google AdSense. High-quality content not only attracts and retains visitors but also plays a significant role in determining the types of ads Google serves, directly impacting ad relevance and earnings. Google AdSense prioritizes websites with original, well-researched, and engaging content that offers value to users, as this fosters longer site visits and higher interaction rates with ads. Quality content improves search engine rankings, driving organic traffic, which is crucial for maximizing ad impressions and revenue. Key attributes of quality content include relevance to the target audience, clarity, accuracy, and originality. Content should address the specific interests and needs of visitors, delivered clearly and concisely, free from grammatical errors. Unique perspectives or insights provide added value and differentiate a site from competitors. Engaging content also encourages user interaction, such as comments, social sharing, and repeat visits, all of which positively affect AdSense performance. Additionally, well-structured, mobile-friendly content enhances user experience, reducing bounce rates and increasing ad viewability.
2. Keyword Optimization

- Keyword optimization is a vital strategy for Google AdSense publishers seeking to maximize website traffic and ad revenue by aligning content and advertising with what users are actively searching for. It involves researching, analyzing, and strategically implementing the most relevant and high-performing keywords within website content and Google Ads campaigns to attract targeted visitors who are more likely to engage with ads. Effective keyword optimization begins with thorough research using tools like Google Keyword Planner to identify terms with a good balance of search volume and competition, including long-tail keywords that capture specific user intent and have higher conversion potential.
- Incorporating keywords naturally into titles, headers, meta descriptions, and throughout the content improves organic discoverability on search engines, driving qualified traffic that enhances AdSense ad impressions and click-through rates. Using keyword variations and related terms broadens reach while maintaining relevance, helping content rank for diverse but related queries. Equally important is the use of negative keywords in paid campaigns to filter out irrelevant traffic, conserving ad spend for clicks with genuine conversion potential.
3. Meta Tags

- Meta tags play a crucial role in website optimization and are key to the success of Google AdSense monetization by influencing search engine rankings and attracting relevant traffic. Meta tags are snippets of text that describe a page’s content; they don’t appear on the page itself but in the HTML code, helping search engines understand what the page is about and how to present it in search results. The most important meta tags include the title tag, meta description, and meta keywords, although the latter has lost significance in most modern SEO strategies.
- The title tag is the main header for search engines and users, appearing prominently in the search results and browser tabs. It should include the primary keyword near the beginning, be concise (ideally under 60 characters), and clearly convey the page’s topic to entice clicks. A well-crafted title tag improves rankings and click-through rates on search engine results pages (SERPs), thereby increasing relevant traffic crucial for Google AdSense success.
4. URL Structure
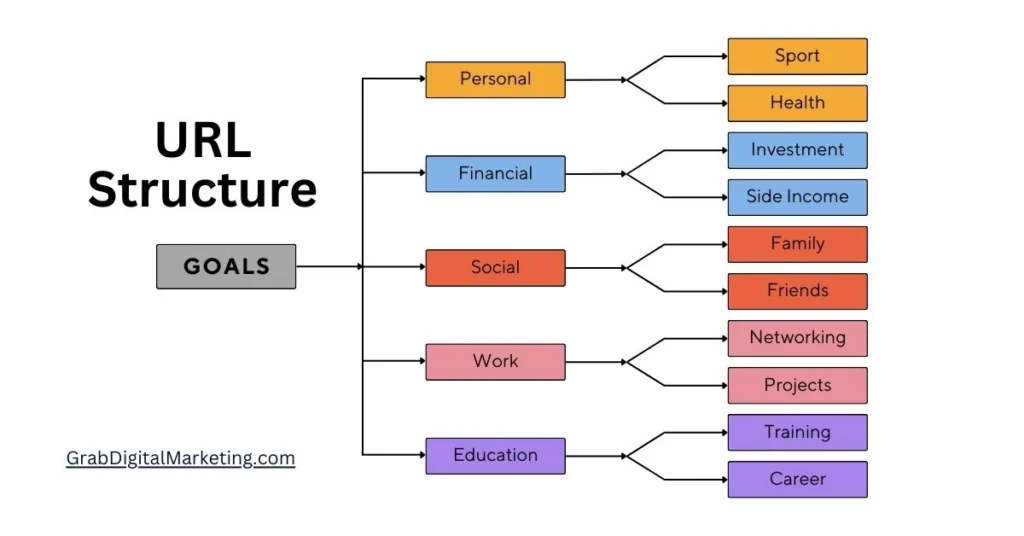
- URL structure is a fundamental aspect of website optimization that significantly impacts both user experience and search engine rankings, making it crucial for Google AdSense publishers aiming to maximize traffic and revenue. A well-structured URL is clear, concise, and descriptive, helping search engines and users easily understand the content and hierarchy of a page. Best practices recommend using readable words instead of long strings of numbers or symbols, with keywords integrated naturally to improve discoverability and relevance in search results. For instance, a URL like example.com/seo-best-practices is far more effective than example.
- Using hyphens to separate words in URLs enhances readability, making them easier to scan for both users and search engine crawlers. Avoiding underscores, special characters, and excessive URL parameters can prevent indexing problems and minimize duplicate content issues, which can dilute SEO value and reduce the volume of traffic crucial for AdSense success. Consistent URL case handling—preferably lowercase—also prevents search engines from treating URLs with different cases as separate pages, consolidating page authority and ranking signals.
5. Internal Linking

- Internal linking is a fundamental SEO strategy that significantly benefits Google AdSense publishers by enhancing site navigation, improving user experience, and boosting search engine rankings, which collectively lead to increased traffic and higher ad revenue. Internal links are hyperlinks directing visitors to other pages within the same domain, creating a web of pathways that guide users through relevant content and avoid dead ends. Strategically placed internal links help distribute link equity (or “link juice”) across key pages, empowering high-priority and monetized content to rank better on search engines while helping Googlebots crawl and index the site more efficiently.
- Effective internal linking starts with identifying valuable content that deserves support, such as cornerstone articles, product pages, or high-converting landing pages. Linking from authoritative pages—like the homepage or popular blog posts—to these targets transfers SEO value, enhancing their visibility and driving more targeted visitors who are more likely to engage with AdSense ads. Contextual internal links embedded naturally within content provide clear value to users by directing them to related or in-depth topics, which keeps visitors on the site longer and reduces bounce rates, vital factors for AdSense monetization success.
6. Image Optimization

Image optimization is a critical aspect of website management that significantly enhances user experience, site speed, and search engine visibility, all of which contribute to greater success with Google AdSense monetization. Optimizing images involves several best practices, starting with using high-quality, relevant images that complement and enhance the website’s content without causing slow load times. Large, uncompressed images can drastically increase page load times, leading to higher bounce rates and reduced ad impressions, which directly negatively affect AdSense revenue. One of the foundational steps in image optimization is compressing images efficiently to reduce file sizes while maintaining visual clarity. Techniques such as using modern formats like WebP, leveraging lazy loading to defer offscreen images, and enabling browser caching improve the overall site speed and user experience, critical factors for SEO and monetization. Additionally, using descriptive, keyword-rich filenames and alternative (alt) text helps search engines understand the image content, boosting organic visibility through image search results and improving the contextual relevance that Google uses for better ad targeting.
7. Mobile Friendliness

Mobile friendliness is an essential factor for Google AdSense publishers aiming to maximize ad revenue and provide an excellent user experience. A mobile-friendly website is designed to display and function seamlessly on smartphones and tablets, ensuring that users can navigate easily, access content quickly, and interact with ads without frustration. Google prioritizes mobile-friendly sites in its search rankings through “mobile-first indexing,” meaning the mobile version of a website is the primary reference for indexing and ranking, making responsiveness critical for visibility and traffic. For AdSense, a mobile-friendly design enhances ad viewability and engagement, which translates to increased ad impressions and higher click-through rates. Key attributes of mobile-friendly sites include responsive design that adapts content layout automatically to fit any screen size, fast load speeds, simple navigation, and clear calls to action suited for touch interfaces. Slow-loading sites or those requiring excessive zooming or horizontal scrolling typically suffer high bounce rates, reducing overall traffic and monetization opportunities. Mobile optimization also involves placing ads strategically in locations that are easily viewable without disrupting user experience, such as at the top of the content or within the text flow. Using mobile-compatible ad formats like responsive or sticky ads helps improve performance on various devices.
8. Page Speed
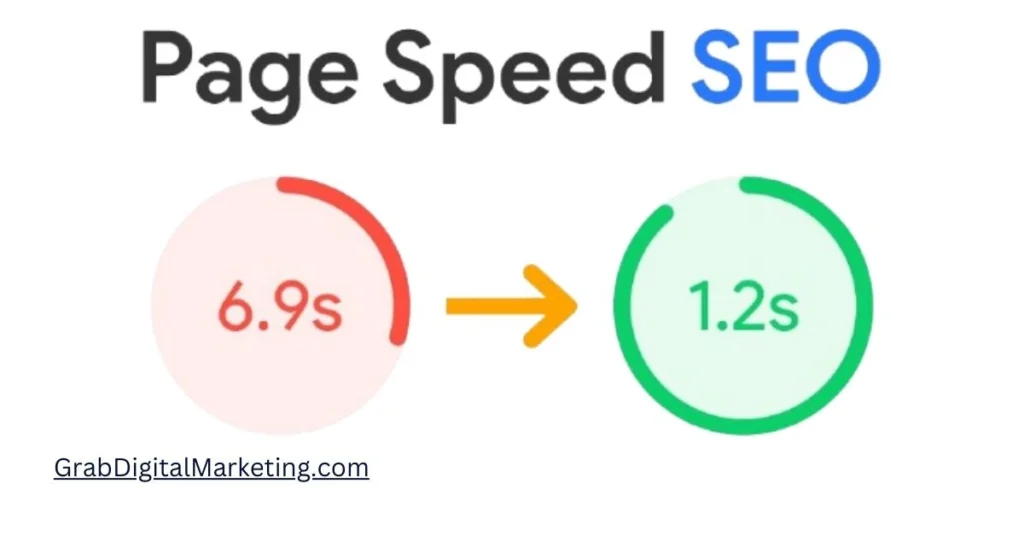
- Page speed is a critical factor for Google AdSense publishers aiming to maximize user experience, search engine rankings, and ultimately, ad revenue. A fast-loading website ensures that visitors stay engaged with the content and ads, reducing bounce rates and increasing the likelihood of ad impressions and clicks. Google’s Core Web Vitals emphasize the importance of metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures how quickly the main content loads, Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which gauges visual stability during loading, and Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which tracks responsiveness. Optimizing these metrics is essential to avoid frustrating users with slow or unstable page experiences that could detract from ad engagement.
- Key strategies to improve page speed include optimizing images by compressing files and using modern formats like WebP, minimizing HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files, and implementing lazy loading to defer loading offscreen images and ads until needed. Utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) reduces latency by serving content from servers closer to users geographically. Browser caching stores site elements on users’ devices, speeding up repeat visits, while HTTPS and HTTP/2 protocols enhance security and loading efficiency.
9. User Experience (UX)
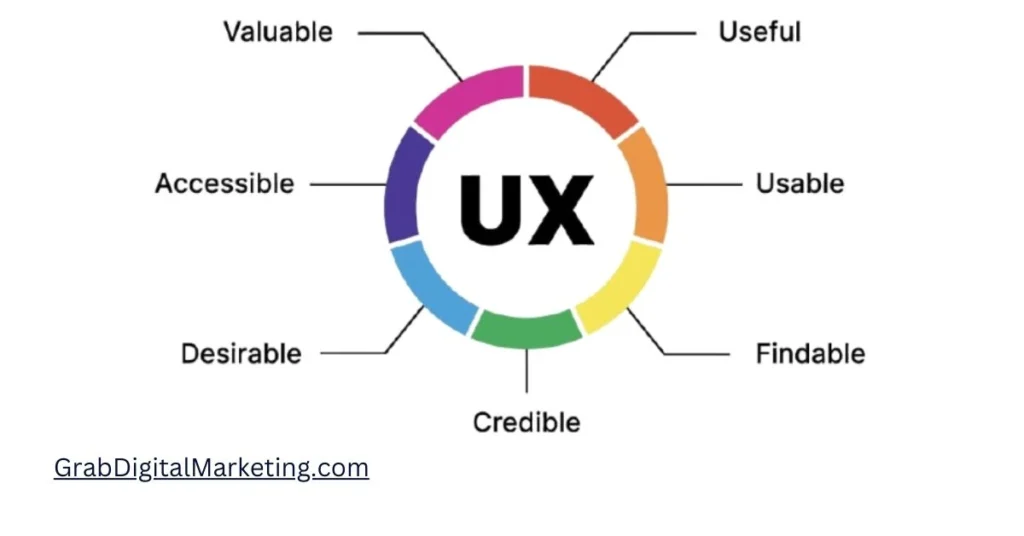
- User Experience (UX) is a critical factor for Google AdSense publishers seeking to maximize both site traffic and ad revenue. UX refers to how visitors perceive and interact with a website, encompassing elements like ease of navigation, site speed, visual appeal, content readability, and overall functionality. A positive user experience encourages visitors to stay longer, explore more pages, and engage with ads, directly increasing the number of ad impressions and click-through rates, which are essential for boosting AdSense earnings.
- To enhance UX, publishers should focus on intuitive site design that allows users to find information quickly and effortlessly. Clear menus, logical content structure, and fast-loading pages minimize frustration and reduce bounce rates. Mobile friendliness is a core component—since most users access websites via mobile devices, ensuring seamless mobile navigation and responsive design is vital for retaining this large audience segment. Incorporating features such as site search and easy-to-use forms also facilitates smoother user journeys and higher conversions, both of which contribute to improved monetization.
10. Social Sharing

- Social sharing is a powerful tool that significantly influences Google AdSense revenue by increasing website visibility, driving targeted traffic, and enhancing user engagement. When website content is shared across popular social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn, it exposes the site to broader audiences who may not have discovered it through traditional search engines. This expanded reach can lead to increased site visits, more page views, and consequently higher ad impressions and clicks—key metrics that boost AdSense earnings. Importantly, the quality of the content being shared plays a vital role in attracting and retaining these visitors; content that resonates well socially tends to generate more genuine interactions and ad engagement, resulting in a higher click-through rate (CTR).
- Beyond simple traffic generation, social sharing fosters a concept known as “social capital,” where active and engaged social networks contribute to sustained interest in a website. This can convert occasional visitors into regular users, thereby increasing session duration and frequency of ad exposure. Studies have shown that websites with strong social media presence often experience a rise in their Google AdSense revenues as social platforms help drive consistent and relevant visitors. For publishers, effectively integrating social sharing buttons and encouraging sharing through calls to action can amplify their content’s reach organically.
11. Schema Markup

- Schema markup is a powerful tool for Google AdSense publishers aiming to enhance their website’s SEO, increase organic traffic, and improve ad revenue. Essentially, schema markup is a type of structured data added to a website’s HTML that helps search engines better understand the content and context of the pages. This enhanced understanding allows search engines to display rich snippets—such as star ratings, event details, product prices, and FAQ panels—in search results, making listings more attractive and clickable for users.
- One of the key benefits of schema markup is its ability to improve click-through rates (CTR) by providing users with more detailed, relevant information upfront in the search engine results pages (SERPs). For example, a recipe page with schema might display cooking times and ratings, which entice users to visit the site over a generic link. This higher CTR drives more qualified traffic, increasing the pool of visitors exposed to Google AdSense ads and thereby boosting revenue potential. Studies show that websites implementing structured data can experience up to a 30-40% increase in organic traffic due to enhanced visibility and richer search presentations.
12. Security
Security is a paramount concern for Google AdSense publishers, as it directly influences user trust, compliance with Google’s policies, and ultimately, the ability to monetize a website effectively. Ensuring a secure website begins with implementing HTTPS encryption through SSL certificates, which safeguards users’ data by encrypting information exchanged between their browsers and the web server. Google actively promotes secure browsing experiences and prioritizes HTTPS-enabled sites in search rankings, enhancing visibility and traffic potential — critical factors for AdSense monetization success. Beyond encryption, maintaining robust account security for Google AdSense itself is vital. Publishers are encouraged to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on their Google accounts to add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Monitoring login activities and using trusted devices further reduces the risk of account compromise, protecting earnings and sensitive payment information from hackers or fraudsters.
13. Analytics and Monitoring

- Analytics and monitoring are fundamental components for Google AdSense publishers who want to optimize their website performance and maximize ad revenue. By leveraging analytics tools such as Google Analytics, publishers gain deep insights into visitor behavior, traffic sources, and how users interact with ads. This data allows understanding patterns such as which pages generate the most traffic, which ad units perform best, and the demographic segments that drive the highest revenue. Integrating Google AdSense with Google Analytics provides a unified view of earnings and traffic metrics, enabling multi-dimensional analysis that helps optimize content strategy and advertising placements.
- Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rates (CTR), impressions, bounce rates, session duration, and revenue per page empowers publishers to make informed decisions. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps identify underperforming pages or ad units, uncover potential issues like invalid clicks, and test new strategies for improvement. Additionally, advanced tools offer automated insights and anomaly detection that alert publishers to sudden changes in traffic or revenue, facilitating timely responses to maintain or enhance performance.
14. Content Freshness

- Content freshness is a crucial factor for Google AdSense publishers aiming to maintain high website rankings, attract repeat visitors, and maximize ad revenue. Fresh content refers to regularly updated, original, and relevant material that keeps a site dynamic and engaging for users. Google’s algorithms prioritize websites that consistently add new or updated content, signaling that the site is active and valuable to users. This preference enhances search engine visibility, leading to increased organic traffic—a key driver for AdSense earnings.
- Maintaining content freshness involves more than just posting frequently; it requires ensuring that existing articles are periodically reviewed and updated with the latest information, statistics, and insights. This ongoing refinement keeps the content accurate and useful, fostering user trust and encouraging longer site visits, which boost ad impressions and user engagement metrics critical to AdSense success. Diverse content formats such as blog posts, tutorials, news updates, videos, and interactive media can also contribute to a perception of freshness and attract a broader audience.
15. Multilingual SEO

- Multilingual SEO is essential for Google AdSense publishers who want to expand their reach across different linguistic markets and attract diverse audiences. It involves optimizing website content to rank well in multiple languages, ensuring users from various regions find the site easily through organic search. A key element of multilingual SEO is using dedicated URLs for each language version, such as example.com/en/ for English and example.com/fr/ for French, allowing search engines and users to differentiate language-specific pages effectively. Proper implementation of hreflang tags signals to Google which version of the content to display in search results based on the user’s language and location, preventing duplicate content issues and enhancing user experience.
- Content localization plays a crucial role in multilingual SEO, going beyond mere translation to adapt messaging, cultural nuances, and keywords to resonate with the target audience authentically. Keyword research should be language-specific to optimize titles, meta descriptions, headers, and image alt text appropriately for each market. This approach improves relevance and click-through rates, driving higher-quality traffic that increases AdSense ad impressions and clicks. Technical SEO considerations include site structure with language switchers, mobile optimization, and use of CDNs to reduce load times for international visitors.

